Signs That It’s Time to Upgrade Your Electrical Panel
There are a number of signs that it’s time to upgrade your electrical panel. These can include frequent circuit tripping and circuit breakers that won’t stay open after a reset. Additionally, new electrical products or remodeling your home may require an upgrade.
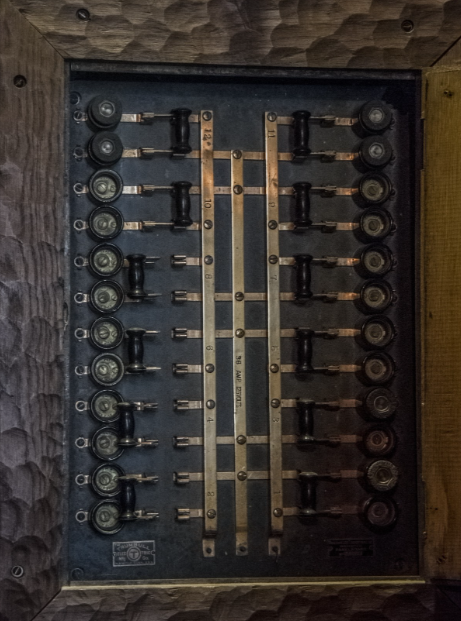

Frequent circuit tripping is a sign of a faulty electrical panel
If the circuit breakers in your home frequently trip, the issue is probably due to a faulty electrical panel. This could also lead to localized power loss. Luckily, circuit breakers are designed to prevent this. They are usually found in a breaker panel that is accessible and not blocked by furniture or storage. If you are unsure of where to find the panel, consider calling a licensed electrician, such as Farryn Electric.
One of the most common causes of tripped circuit breakers is a short circuit. A short circuit occurs when a live or hot wire comes into contact with a neutral or ground wire. This creates a large current and overloads the circuit. This can lead to sparks, smoke, and a popping sound. In addition to tripped circuit breakers, short circuits can also be the result of damaged or slipped wires or cables.
Fortunately, this problem is fairly easy to diagnose. If you notice frequent circuit tripping in an area of your home, you can check it by unplugging the affected devices, flipping the breaker back on, and then plugging them back in. You should note the last thing you plugged in when the circuit breaker tripped, and unplug everything else.
Circuit breakers that won’t stay open after a reset
If your circuit breakers won’t stay open after a reset, this is probably a sign that your electrical panel isn’t functioning correctly. You can try to reset a tripped breaker by moving the switch to the “Off” position, then pushing the handle forward to the “On” position. This should reset the breaker. If the circuit breaker remains closed after a reset, you may need to replace the entire panel.
Before you can replace your entire electrical panel, you must first identify the cause of the breaker’s tripping. To identify the cause of a circuit breaker’s tripping, you must unplug any appliances that are connected to the breaker.
Another way to determine if a circuit breaker is faulty is to check the voltage levels in your electrical panel. If the voltage level is low, the breaker could cause electrical problems and even a fire hazard. In addition, if you smell a burning smell coming from the panel, the breaker is probably faulty. Lastly, a faulty circuit breaker can also be hot to the touch. If you notice these signs, call a professional electrician to come inspect the panel.
Increased electrical load
Electrical panels are a vital part of a home. They distribute electricity and route it to the areas in the home that need it. Over time, they may show signs of wear and tear. This can include things like flickering lights or a strange smell. If you suspect that you need to upgrade your panel, you should consult an electrician. The electrical panel is the warehouse where electricity is sent to various parts of the house. Hence, it is imperative that you upgrade it before it becomes useless.
Upgrading your electrical panel is an investment in the safety of your family and the value of your home. The electrical panel is an integral part of your home’s mechanical system, and it requires regular maintenance just like your HVAC and plumbing systems.
Upgrading your electrical panel is a complex process that requires a licensed electrician. The procedure can take anywhere from eight to ten hours, depending on its complexity. If you are planning to sell your home in the near future, a new electrical panel can help you maximize your asking price. It may also help you reduce your home’s time on the market during a cold selling season.
Remodeling or adding new electrical products could be a sign that it’s time to upgrade your electrical panel
An outdated electrical panel is a fire hazard. If you have frequent fuses tripping, it might be time to upgrade. Moreover, outdated panels may not be up to current safety standards. Fuse-based panels were common in homes built before 1960. While they may be simpler to operate, they may pose greater risks for a house fire.
Your electrical panel is a critical part of your home’s electrical system. It routes electrical currents throughout the home and connects the main power line to each room. The number of circuits on your electrical panel will determine the amount of power your home is able to handle.
An outdated electrical panel may have limited space to handle the new electrical products that you are adding. In addition, older homes may have aluminum wiring or rusted panels. These problems can affect the safety of electronics and appliances in your home. It is best to have an electrical panel upgraded by a licensed electrician.